What Is Restrictive Early Action?
Understanding college admissions can be like solving a puzzle, with each part showing a different way to get accepted into college. Restrictive Early Action (REA) is one of these ways. It’s a special kind of early application where students apply sooner than usual. REA is called “restrictive” because it usually means you can’t apply early to many other schools.
This blog post has two main goals. First, it wants to make REA easy to understand. It will explain what REA is and correct any wrong ideas people might have about it. Second, it aims to show how REA fits into applying for college. By the end of this post, you should know a lot more about REA and how it works.
It’s really important to understand REA if you’re thinking about college. For some students, REA can be a good way to show a college that it’s their first choice, which might help them get in. But for others, REA might not be the best idea, especially if they want to apply to many places or need to see different financial aid offers.
Knowing what Restrictive Early Action is can help students and their families make better choices when applying to college. This post is here to help make the college application process less stressful and more clear, giving families the information they need to feel confident and well-informed.
The Basics of Restrictive Early Action
Understanding each admissions option is crucial when navigating the world of college admissions. Restrictive Early Action (REA) stands out as a unique path. Let’s break down what REA really means, how it’s different from other application types, and the typical timeline for REA applications.
What is Restrictive Early Action?
Restrictive Early Action is a type of early college application process. Here’s the deal: you apply early, usually in November of your senior year, and get your admission decision early, too, often in December. The “restrictive” part is important. It means you agree not to apply to other colleges under an Early Action or Early Decision program.
However, REA is non-binding. This means if you’re accepted, you’re not obligated to attend. You have until the regular decision deadline, typically May 1st, to decide. This gives you time to weigh your options, compare financial aid packages, and make a well-informed decision.
Key Terms Associated with Restrictive Early Action
Now that we have a better understanding of what REA is, let’s dive into some key terms associated with this early admission process:
- Early Action (EA): This is a college admission process where students apply before the regular admission cycle and receive an admissions decision earlier. It is similar to REA but without the restriction of only applying early to one.
- Restrictive Early Action (REA): As we’ve discussed, this is a variation of EA where students are prohibited from applying early, in any form, to other universities. It offers the advantage of showing a higher level of commitment to the chosen institution.
- Non-binding: This refers to an admission process where, if accepted, students aren’t required to commit to the institution. It allows students to explore other options and make an informed decision.
- Deferral: Sometimes, instead of receiving an immediate decision, a college may defer an early action application to the regular admission pool. This means that the application and the regular pool of applicants will be reconsidered, and a final decision will be made later.
Understanding these terms can help you navigate the college admissions process more effectively and make informed decisions about which strategies to pursue.
Common Misconceptions About REA
When you’re a high school student thinking about college, you might hear about Restrictive Early Action (REA) and get some mixed messages about what it really means. Let’s clarify some common misconceptions about REA so you can understand it better.
“REA Increases Your Chances of Getting In”
A lot of students think that if they apply REA, they have a better chance of getting accepted. This isn’t always true. REA applicants often have really strong grades and achievements, so the competition is tough. Some colleges might accept more REA students, but this doesn’t mean it’s easier to get in. It’s important to apply REA only if you’re really ready and sure about the college.
“If You Get Accepted REA, You Must Go There”
This is a big misunderstanding. REA is not a binding agreement. That means if the college says yes, you don’t have to go there. You have until May 1 to decide. This is different from Early Decision (ED), where you must go to the college if they accept you.
“You Can’t Apply Anywhere Else if You Choose REA”
Some students think that if they apply to a college REA, they can’t apply to any other college at all. This isn’t true. You can’t apply early to other private colleges, but you can still apply to other colleges under their regular decision plans. Also, you can apply early to public universities and colleges outside the U.S. without any binding agreement.
“REA is Only for Certain Types of Students”
Some students might think REA is only for certain kinds of students, like those who are super sure about their first-choice college or who have lots of achievements. While it’s true that REA is a good fit for students who have a clear first choice, it’s open to anyone who meets the college’s requirements. You don’t have to be a certain type of student to apply REA.
“REA Means a Faster Decision, So It’s Less Work”
Applying REA does mean you’ll hear back from the college earlier, but it doesn’t mean the application process is easier. You still need to put the same effort into your application as you would for Regular Decision. This means strong essays, good grades, and maybe standardized test scores, depending on the college.
“If You’re Deferred in REA, You Won’t Get In”
Being deferred means the college will look at your application again with the Regular Decision applications. Some students think this means they won’t get accepted later, but that’s not true.
Being deferred doesn’t mean no; it just means to wait. You still have a chance to get accepted.
“REA is the Same at Every College”
Each college has its own rules for REA. Some might have more restrictions than others. It’s important to read the specific rules for REA at each college you’re interested in.
So, when you’re thinking about applying to college and considering REA, remember these points. It’s all about finding the right fit for you and understanding the rules and chances. Make sure you’re making informed decisions about where and how you apply.
Alternatives to REA
When thinking about applying to college, it’s important to know all the different ways you can apply. Restrictive Early Action (REA) is just one option. There are others like Regular Decision, Rolling Admissions, and Early Decision. Let’s look at these and see how they compare to REA.
Regular Decision is the most common way students apply to college. With this option, you send in your application by a set deadline, usually around January. Then, you wait until spring to hear back from the college. The good thing about Regular Decision is that it gives you more time to work on your application and to think about where you want to apply. You’re also not tied to one college if you get accepted, so you can choose from all the colleges that accept you.
Rolling Admissions is different because there isn’t a strict deadline. Colleges that use this system review applications as they come in and make decisions throughout the admission season. This means you could hear back from them soon after you apply. Rolling Admissions can be less stressful because you don’t have to wait until a specific time to find out if you got in. But, it’s still a good idea to apply early because spots might fill up.
Early Decision is a bit like REA because it’s also an early application process. The big difference is that Early Decision is binding. This means if the college accepts you, you have to go there. This option is good for students who are really sure about their first-choice college. But, it’s not great if you want to compare different colleges or financial aid offers.
Now, how do these compare to REA? Well, REA is also an early application, but it’s not binding like Early Decision. This means you can still look at other colleges if you get accepted. But, REA often stops you from applying early to other private colleges. So, it’s a good choice if you have a favorite college but still want to keep your options open.
Each option has its pros and cons, and the best choice depends on what you want and need from the college application process. Some students like the idea of getting it done early with REA or Early Decision. Others prefer the flexibility of Regular Decision or Rolling Admissions. It’s all about what works best for you and your goals for college.
How Does REA Differ from Early Decision and Regular Decision?
REA is often confused with Early Decision (ED), but they’re quite different. Early Decision is binding. If you apply ED to a college and get accepted, you’re committed to attending that college. This is a significant commitment and should be considered carefully. Regular Decision, on the other hand, is the standard application process. You apply by a later deadline, usually in January or February, and receive your admission decision in the spring.
REA sits between these two. It’s like Early Decision because you apply early and demonstrate a serious interest in a college. But it’s like Regular Decision because it’s non-binding. You’re free to choose another college even if you’re accepted through REA.
Typical Timeline for REA Applications
Understanding the REA timeline is key. Here’s what it typically looks like:
- Preparation Year (Junior Year): Research colleges, take standardized tests, and draft your application materials.
- Application Submission (Early Senior Year): Submit your REA application by early November.
- Admission Decisions Released (Mid-December): Colleges send out REA decisions. You could be accepted, deferred to the regular decision pool, or denied.
- Regular Decision Deadline (January-February): Submit regular decision applications if deferred or still considering other options.
- Final Decision (By May 1st): If accepted through REA, decide whether to attend by this date.
The REA process demands early preparation and clarity about your college preferences. It’s a pathway that can lead to early success in your college admissions journey, but it requires careful consideration and strategic planning. As you mull over your options, remember that choosing the right application process can set the tone for your entire college experience.
Who Offers Restrictive Early Action?
Restrictive Early Action (REA) is a term that can confuse students and parents during the college admissions process. Yet, it’s a pivotal concept that could shape your college journey. So, who’s in the game?
The answer is a select group of prestigious institutions. These schools often employ REA to attract top-tier students who are highly committed to attending. It’s a win-win situation: the colleges get to boost their yield rates, and the students get an early shot at their dream schools. But remember, REA isn’t as widespread as other admissions options like Early Decision or Regular Decision.
Prominent Colleges and Universities That Offer REA
Harvard, Stanford, and Yale are often the first names that come to mind. These Ivy League and Ivy-adjacent schools are the flag bearers of REA, setting the tone for its exclusivity and allure.
Below are the following top schools in the US that offer Restrictive Early Action with its corresponding deadline and notification date for the admissions cycle 2023-2024:
Schools from the Top 50 National Universities Offering Restrictive Early Action for 2023-2024
|
School Name |
Application Deadline |
Notification Date |
| Harvard University | November 1, 2023 | December 15, 2023 |
| Stanford University | November 1, 2023 | December 16, 2023 |
| California Institute of Technology | November 1, 2023 | December 10, 2023 |
| University of Notre Dame | November 1, 2023 | December 16, 2023 |
| * Princeton University | November 1, 2023 | December 15, 2023 |
| * Yale University | November 1, 2023 | December 15, 2023 |
Note: * Although it offers Single-Choice Early Action, it’s still the same as REA
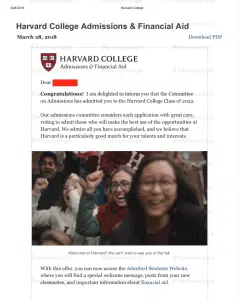
Harvard University
At Harvard, you can apply early by November 1 and get your decision by mid-December. This early option is not a binding one, meaning you don’t have to go to Harvard if they accept you. You have until May 1 to make up your mind. When you choose to apply early to Harvard, you can’t do the same at other private colleges. But you’re free to apply to public universities, military academies, or colleges outside the U.S. without any binding agreement. You can also apply to other universities under their Regular Decision or Early Decision II programs. If Harvard puts you on a waitlist in the Early Action round, you can then apply to a binding Early Decision program at another college. Regardless of how you apply, Harvard promises to meet your financial needs.
Stanford University
Stanford’s non-binding Restrictive Early Action is for students who see Stanford as their first choice and have excelled in challenging academic courses. The application deadline is November 1. Here, you can’t apply early to private colleges or to public universities’ binding early programs. However, you can apply to other colleges under their regular decision. If Stanford defers you in the Early Action round, you can opt for an Early Decision II plan at another college.
California Institute of Technology
Restrictive Early Action at Caltech is for students who really want to go to Caltech more than any other university. It’s a way to apply early and find out sooner if you get in, but it’s not a promise that you have to go there if they accept you.
You can still see what other colleges offer, especially when it comes to financial aid, by applying to them for their regular decision dates. You need to send in your REA application by November 1, and Caltech will let you know if you got in, need to wait a bit longer, or didn’t get in by the middle of December. If you’re accepted, you have until May 1 to decide whether you want to go to Caltech.
University of Notre Dame
Notre Dame offers a non-binding Early Action option. You can apply to other Early Action programs at both private and public colleges but not to any binding Early Decision programs. You don’t need to express a first-choice preference for Notre Dame and can wait until May 1 to make your decision. In rare cases, students may switch their Regular Decision application to an Early Action one by November 15.
Princeton University
Princeton has a Single-Choice Early Action process. It’s nonbinding, so you don’t have to commit to going there if they accept you. The deadline is November 1, and if accepted, you have until May 1 to let them know your decision. Like Harvard, you can’t apply early to other private colleges in the U.S. However, applying to any public institution or service academy that doesn’t require an early commitment, any international institution with a nonbinding decision, or any college with a nonbinding rolling admission process is okay.
Yale University
Yale’s Single-Choice Early Action is unique. You can’t apply to any other school’s early action or early decision program, with a few exceptions. You can apply to colleges with non-binding rolling admission programs, public institutions with non-binding admission, another college’s Early Decision II program (if the notification is after January 1), and another college’s Early Action II program or institutions outside the U.S.
If you’re setting your sights on the very best colleges and universities – the top-tier, elite institutions that are often regarded as the pinnacle of higher education – then getting a good grasp on Restrictive Early Action (REA) might be incredibly important for you. REA could act as your ‘golden ticket’, a special advantage or key that unlocks the door to these prestigious schools.
Is Single-Choice Early Action and Restrictive Early Action the Same?
Single-Choice Early Action (SCEA) and Restrictive Early Action (REA) are essentially the same. Both terms describe an early college application process that allows a student to apply early to one institution only. Under this plan, the student agrees not to apply to any other school’s early decision or early action program. However, they are still free to apply to other schools under regular decision and are not committed to attending the Early Action school if accepted.
The main difference lies in the terminology used by different colleges. Some institutions prefer the term “Single-Choice Early Action” to emphasize the exclusivity of the choice, while others use “Restrictive Early Action” to highlight the limitations on applying to other early programs. Despite the different names, the core principles of the application process remain the same.
What are the Advantages of Restrictive Early Action?
As you weigh your college application options, understanding the benefits of Restrictive Early Action (REA) can be pivotal. REA has several advantages, from early admissions results to potentially improved acceptance rates. Let’s explore these benefits, supported by statistics and real student experiences.
1. Early Admissions Results
One of the most appealing aspects of REA is the early response from colleges. Imagine submitting your application in November and receiving a decision by December. This quick turnaround is a significant advantage. It allows you to know where you stand with your top-choice college well before regular decision applicants. If accepted, you can enjoy the rest of your senior year with the peace of mind of knowing your college future is secured.
2. Reduced Stress by Early Senior Year
The senior year of high school is often marked by a mix of excitement and stress, especially when it comes to college applications. REA can reduce this stress significantly. By applying early and receiving a decision early, you can avoid the prolonged anxiety that often accompanies the regular decision process. This means more time to focus on your final year of high school, enjoy your activities, and prepare for the transition to college.
3. Improved Chances of Acceptance
One of the most debated advantages of REA is the potential for improved acceptance rates. While this can vary by college, some statistics suggest that REA applicants might have a slight edge. For instance, at some prestigious universities, REA acceptance rates have been reported to be slightly higher compared to regular decision rates. However, it’s important to note that this doesn’t necessarily mean REA is an easier route. Often, the applicant pool for REA is highly competitive, comprising students who are very confident in their qualifications and their choice of college.
REA offers several benefits, from early results and reduced stress to potentially better acceptance odds. These advantages make it an attractive option for many students. However, assessing whether it aligns with your readiness, qualifications, and confidence in your college choice is crucial. As you plan your path to college, consider if REA could be the right step for you.
Considerations and Limitations of REA
While Restrictive Early Action (REA) has perks, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. It comes with certain limitations and demands careful consideration. Let’s delve into the restrictions on applying to other schools, the impact on financial aid comparison, the commitment level required, and scenarios where REA might not be the ideal choice.
1. Restrictions on Applying to Other Schools
One of the key restrictions of REA is its impact on your ability to apply early to other institutions. Under REA, you agree not to apply to any other college or university under an Early Decision or Early Action program. This can limit your early application options, confining you to just one early application at your REA school. You can still apply to other schools under Regular Decision, but you won’t hear back from those until spring. This restriction requires you to be quite confident in your REA school as your top choice, as you’re effectively putting all your early application eggs in one basket.
2. Limited Ability to Compare Financial Aid Offers
Applying REA can also impact your ability to compare financial aid offers. Since REA decisions are made early and are non-binding, you’ll know if you’re accepted by December. However, you may not receive your financial aid package until later, and you can’t compare it with offers from Regular Decision applications which come in the spring. This can be a significant drawback if financial considerations are a top priority for your family. The inability to compare offers side by side might lead you to make a less informed decision financially.
3. The Commitment Level Required
REA demands a high level of commitment. While it’s not binding like Early Decision, applying REA to a college indicates a strong interest in that institution. You need to have a clear first choice and be almost certain that this is the school you want to attend, provided the financial and other conditions are right. This level of certainty might be challenging for some students who are still exploring their options or may have several top-choice schools.
Scenarios Where REA Might Not Be the Best Choice
Considering these limitations, there are scenarios where REA might not be your best bet:
- If you’re still exploring options: If you’re not 100% sure about your top choice, or if you have multiple colleges you’re equally interested in, REA can be limiting.
- If financial aid is crucial: If comparing financial aid packages is essential for your decision, REA’s early decision timeline can be a disadvantage.
- If your application needs more time: If you think your application (like test scores, grades, or extracurriculars) will be stronger with a few more months of senior year under your belt, waiting for Regular Decision might be wiser.
In summary, while REA can be an excellent pathway for some, it’s not without its limitations. The restrictions on applying to other schools, the potential challenges in comparing financial aid, and the high commitment level required are important factors to consider. REA can be a powerful tool in your college application arsenal, but ensuring it aligns with your personal circumstances, preferences, and college goals is crucial.
Strategy and Decision-Making
Deciding whether Restrictive Early Action (REA) is the right path requires strategic thinking and a deep understanding of your personal, academic, and financial situation. Here’s how you can approach this decision-making process to determine if REA aligns with your college aspirations.
How to Decide if REA is Right for You
To ascertain if REA suits your college journey, consider the following:
- Check If You’re Ready: Look at your grades and the activities you do outside of school. Are they really good? Remember, students who apply early usually have very strong grades and achievements. Think about whether your grades and activities are strong enough to stand out in this group.
- Think About Your Favorite College: Is the college you’re applying to early (through REA) your number one choice? With REA, you can only apply early to one college, so it should be the one you want to attend the most. If you get in, you can still say no later, but you can’t apply early to other places.
- Know What It Means to Choose REA: If you decide to apply REA, it shows the college that you’re interested in going there. It’s not a promise like some other early plans, where you have to go if they accept you. But it still shows that you’re serious about this college.
So, deciding on REA means you need to be sure you’re ready, it’s your top college choice, and you understand what it means to show that college you’re really interested in them.
Balancing REA with Other College Application Options
Managing REA alongside other application options requires a balanced approach:
- Plan for Multiple Scenarios: If you’re not accepted through REA, be prepared to apply to other colleges through Regular Decision. Have your list of colleges ready.
- Keep Improving Your Profile: Use the time between your REA application and regular decision deadlines to bolster your application – improve grades, take part in meaningful extracurricular activities, and gather strong recommendations.
- Stay Informed: Keep track of all application deadlines and requirements for your other prospective colleges, ensuring you’re ready to proceed irrespective of the REA outcome.
Consulting with Guidance Counselors or College Consultants
Guidance counselors and college consultants can provide valuable insight:
- Leverage Their Experience: These professionals understand the nuances of college admissions and can offer tailored advice based on your profile and preferences.
- Discuss Your Options: They can help you weigh the pros and cons of REA versus other application processes, considering your specific circumstances.
- Gain Perspective: Sometimes, an external, professional perspective can help clarify your decision and strategy.
Considering Financial, Academic, and Personal Factors
A holistic approach to your decision includes:
- Financial Considerations: If comparing financial aid offers is crucial, remember REA limits this ability. Ensure you’re comfortable with potentially accepting an offer without comparing it with others.
- Academic Fit: Does the REA school offer the academic programs, resources, and opportunities that align with your career goals and interests?
- Personal Readiness: Are you ready to commit early to a college? This includes being emotionally and academically prepared for the transition.
Deciding on REA is not just about meeting early deadlines; it’s about aligning your application strategy with your overall college aspirations and personal circumstances. Take the time to reflect on your readiness, preferences, and goals. Consult with professionals, and consider all factors impacting your college journey. Remember, the right strategy is one that not only maximizes your chances of success but also aligns with your long-term educational and personal objectives.
Preparing for a REA Application
Applying for college, especially through Restrictive Early Action (REA), is a big step. You need to show your best self. Here’s a guide to help you prepare, covering academic requirements, extracurricular activities, personal statements, recommendation letters, and staying organized.
1. Academic Requirements and Preparation
Your grades and classes matter a lot. For REA, colleges look at your performance until junior year and the start of senior year. Here’s how to get ready:
- Stay on Top of Grades: Good grades in tough classes show colleges you’re ready for their challenges. Take Advanced Placement (AP) or International Baccalaureate (IB) classes if you can.
- Ace Your Tests: Prepare for the SAT or ACT early. Aim to finish these tests by the summer before senior year.
- Know Your Target College’s Standards: Each college has its own expectations. Make sure your grades and test scores match or exceed these.
2. Extracurricular Activities and Their Impact
Colleges want to see what you do outside class. They look for leaders and people who make a difference. Here’s what counts:
- Quality Over Quantity: It’s better to be really involved in a few activities than to do many things without much involvement.
- Highlight Your Achievements: Show how you’ve grown and what you’ve accomplished in your activities.
- Align with Your Interests: Choose activities that match your interests and potential major. This shows your commitment and focus.
3. Crafting a Compelling Personal Statement
Your personal statement is your chance to tell your story. It’s where you can stand out. Here’s how to make it great:
- Be True to Yourself: Write about things that matter to you. This makes your essay genuine and engaging.
- Use Specific Examples: Don’t just say you’re a leader or hard worker. Show it with real-life examples.
- Connect to the College: Explain why you’re a good fit for the REA college. Show them why you belong there.
4. Getting a Strong Letters of Recommendation
Recommendation letters can give a big boost to your application. They offer a view of you from others’ eyes. Here’s how to get good ones:
- Pick the Right People: Choose teachers who know you well. They can write about your strengths in detail.
- Help Them Help You: Give them a summary of your accomplishments and goals. This can guide them in writing your letter.
- Ask Early: Don’t wait until the last minute. Give your teachers plenty of time to write a good letter.
5. Deadlines and Organizational Strategies
Staying organized is key to a smooth application process. Here’s how to manage it:
- Keep Track of Dates: Know when everything is due – applications, tests, recommendation letters, and financial aid forms.
- Start Early: Begin your college application journey in your junior year. This gives you more time to prepare.
- Set Regular Goals: Have weekly or bi-weekly targets. This keeps you on track and avoids last-minute rushes.
Preparing for a REA application takes effort, planning, and dedication. Focus on showing your academic strength, involvement in meaningful activities, crafting a personal story in your essay, securing impactful recommendation letters, and being organized. Remember, this is more than just an application – it’s a showcase of your achievements and a step towards your future. Make it count!
What If You’re Accepted, Deferred, or Rejected?
When you apply to college through Restrictive Early Action (REA), there are three possible outcomes: you might get accepted, deferred, or rejected.
Each of these outcomes means different things, and you should handle them in different ways. Let’s talk about what you can do in each situation.
Understanding and Responding to an Acceptance
Celebration is in order! Being accepted through REA is a significant achievement. It means your top-choice college sees you as a great fit for their community. This is the moment to savor your success and share the good news with family and friends. Here’s what to do next:
- Celebrate Your Success: First, take a moment to feel proud of yourself. Getting accepted is a big deal, and you’ve worked hard for it.
- Think About Your Choice: Now, think carefully. Is this college really the best place for you? Think about the classes they offer, what life is like on campus, where it’s located, and how much it costs.
- Look at Financial Aid: If the college offers you money to help pay for school, look at it closely. Make sure it’s enough. If it’s not, you might need to talk to the college or look for other scholarships.
- Tell Other Colleges: If you decide this college is where you want to go, let any other colleges you applied to know that you’re not coming. This helps them and other students who are waiting to hear back.
After the initial excitement settles, it’s time to start planning for your college life. This means researching housing options, understanding your financial aid package, and looking into courses and majors. You might also want to connect with future classmates through social media groups or college forums. Preparing early can ease the transition to college life and help you hit the ground running when you arrive on campus.
Strategies for Dealing with a Deferral
A deferral means the college is still considering your application but hasn’t made a final decision yet. It’s natural to feel a bit disappointed, but it’s important to remember that a deferral is not a rejection. You still have a chance to be accepted in the regular admissions round. Here’s what to do:
- Stay Hopeful: Remember, being deferred isn’t the same as being rejected. You still have a chance to get in.
- Update Your Application: If you’ve done anything new or impressive since you applied, like getting better grades or winning an award, let the college know. It could help your chances.
- Keep Applying Elsewhere: Make sure you have other options. Apply to different colleges, too, just in case.
Use this time to strengthen your application. Update the college with any new achievements or improved grades. Continue to demonstrate your interest in the college by visiting the campus or attending virtual events if possible. Meanwhile, focus on your regular decision applications to other colleges. Keep your options open and continue to put effort into each application.
Coping with and Learning from a Rejection
Facing rejection is tough, but it’s a part of the journey that many successful people have navigated. It’s okay to feel upset or disappointed, but don’t let it diminish your self-worth or derail your college plans. Remember, college admissions decisions often reflect a college’s needs and priorities as much as your qualifications. Here’s how to handle it:
- It’s Okay to Be Upset: It’s normal to feel sad if you don’t get in. Give yourself time to feel those feelings.
- Learn from It: Ask the college why they didn’t accept you if you can. Their feedback can help you make your applications to other colleges better.
- Don’t Give Up: Keep focusing on your other college applications. Use this as a chance to make those applications even stronger.
Redirect your energy towards your regular decision applications. You have a diverse range of colleges to explore, each with unique opportunities and experiences to offer. Stay engaged in your current academic and extracurricular activities. Maintaining your performance is crucial, as colleges will look at your entire high school record.
Remember that it’s just one part of your journey, no matter what happens with your REA application. Whether you’re celebrating, waiting a bit longer, or looking at other options, keep your head up and stay focused on your future. You have lots of opportunities ahead of you!
Next Steps After Each Decision Outcome
Regardless of the outcome, keep moving forward with your college journey. If accepted, start preparing for your college life. If deferred or rejected, concentrate on your regular decision applications. Maintain your academic and extracurricular performance, and stay optimistic.
The college admissions process is just one phase of your academic journey and life. Learn from each experience and use it to grow stronger and more adaptable. Talk about your feelings with family, friends, or a counselor – sharing your experiences can provide comfort and perspective.
Your reaction to the outcomes of your application can also be a learning experience. It teaches you about handling success and setbacks, a skill that will be valuable throughout your life. College is about new beginnings and growth, and how you handle your REA decision can be a stepping stone towards that growth.
Whether positive or otherwise, the outcome of your REA application is a significant step in your college admissions journey. Each scenario offers a chance to learn, grow, and make informed decisions about your future. Remember, the path to college is not just about where you get in but also how you adapt and respond to the outcomes. Stay focused, resilient, and positive, and you’ll navigate this journey successfully.
Final Thoughts
Embarking on your college journey with the Restrictive Early Action (REA) option in mind, you’ve explored a path filled with unique opportunities and challenges. From understanding the basics of REA, its benefits such as early decisions and potentially higher acceptance rates, to navigating its limitations like application restrictions and financial considerations, you’re now equipped with crucial insights.
Preparing a standout REA application involves academic excellence, impactful extracurriculars, compelling personal statements, and strong recommendations. Each decision, whether it’s an acceptance, deferral, or rejection, brings you one step closer to your ultimate goal. Embrace each outcome as an opportunity to learn and prepare for the next step in your journey. Stay focused on your goals, keep up your hard work, and remain open to the array of opportunities that lie ahead.
As you stand at the threshold of this exciting phase, remember your college journey is as unique as you are. It’s not just about getting into a college but finding the right fit for your aspirations and growth.
Ready to Navigate the Maze of College Admissions? AdmissionSight Is Here to Guide You!
You’ve just unraveled the complexities of Restrictive Early Action and are probably weighing its pros and cons. It’s a lot to take in. The college admissions process is a labyrinth, filled with deadlines, decisions, and stress. But what if you had a seasoned guide to lead you through this maze, ensuring you make the right turns at every crossroad?
That’s where AdmissionSight comes in. With our expertise in college admissions, we specialize in helping students like you make informed decisions that can shape your academic future.
Whether it’s choosing between REA, Early Decision, or Regular Decision, crafting that perfect essay, or preparing for interviews, we’ve got you covered. Our personalized consulting services are designed to meet your unique needs, ensuring you stand out in the highly competitive admissions landscape.
So, why navigate this journey alone when expert help is just a click away? Take the first step towards securing a spot at your dream college. Contact AdmissionSight today, and let’s turn your college aspirations into reality!