All About Rube Goldberg Machine
What is a Rube Goldberg machine?
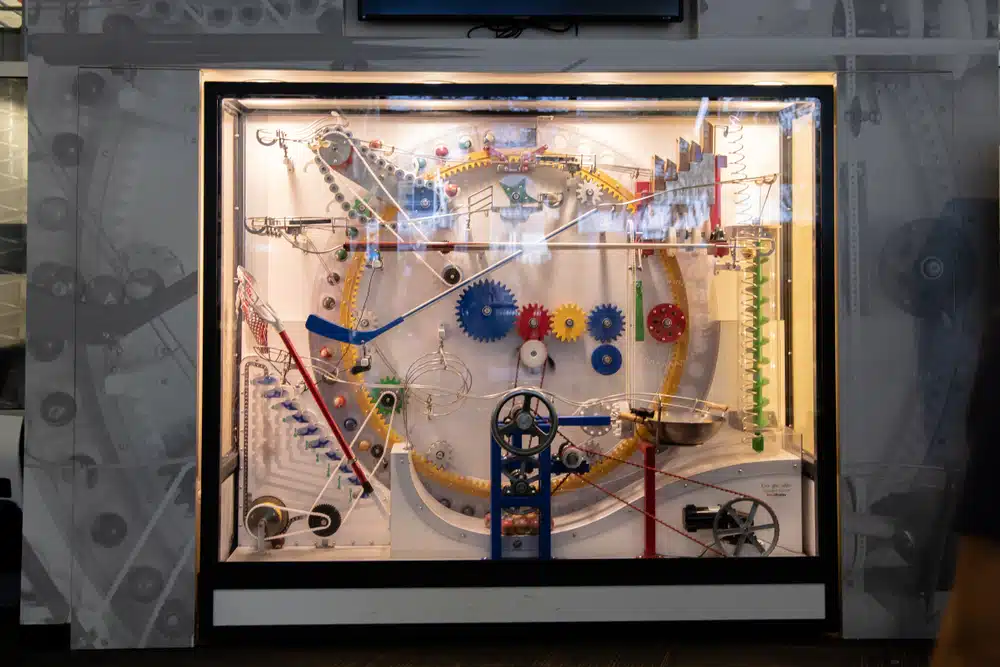
What is a Rube Goldberg machine? A Rube Goldberg machine is a complex contraption that uses a chain reaction of actions to accomplish a simple task, such as turning on a light switch or pouring a bowl of cereal. The machine is named after the American cartoonist Rube Goldberg, famous for creating humorous drawings of such machines in the early 20th century.
Rube Goldberg machines typically involve a series of simple machines such as pulleys, levers, inclined planes, and everyday objects such as marbles, dominoes, and toy cars. These objects are connected in a chain reaction, with each action triggering the next until the final task is accomplished. Rube Goldberg machines often incorporate creative and unexpected elements, like animals or musical instruments, to add entertainment value.
Designing and building a Rube Goldberg machine requires high levels of creativity, problem-solving skills, and attention to detail. They are often used in educational settings to teach STEM concepts and promote teamwork and innovation. Rube Goldberg machines have also become popular in pop culture, appearing in music videos, advertisements, and movies.
The history of Rube Goldberg machines
Rube Goldberg machines are named after the American cartoonist and inventor Rube Goldberg, who was born in San Francisco in 1883. Goldberg was a prolific cartoonist who started his career in the early 1900s and became famous for his humorous drawings that depicted complicated machines designed to perform simple tasks. These machines would later be called “Rube Goldberg machines.”
Goldberg’s cartoons were popular in newspapers across the United States, and his machines became a cultural phenomenon. The machines were often depicted performing tasks such as turning off a light switch, opening a door, or pouring a cup of coffee. Still, the contraptions that Goldberg designed were far more elaborate and fantastical.
In 1931, Goldberg won the Pulitzer Prize for editorial cartooning, cementing his place in American cultural history. Over the years, his machines continued inspiring people and appeared in countless books, cartoons, and movies.
Today, these machines are often used as educational tools to teach children about physics, engineering, and problem-solving. They have also become a popular form of entertainment, with Rube Goldberg competitions and events held around the world. In 1987, Purdue University started an annual contest, which challenges teams of students to design and build a machine that can perform a specific task using a minimum of 20 steps. The contest has since grown in popularity and now attracts teams from universities and schools around the world.
How does a Rube Goldberg machine works?
How does a Rube Goldberg machine works? The key to understanding how a Rube Goldberg machine works is the chain reaction concept. A chain reaction occurs when events trigger each other sequentially, like falling dominoes. In this machine, each component is designed to trigger the next component, and so on, until the final task is accomplished.
The science behind this machine lies in physics principles, particularly in energy, force, and motion. It is designed to create a chain reaction of events, where each event triggers the next one in a series until the final event or task is accomplished.
The first principle of physics involved in such a machine is energy transfer. Each machine component is designed to transfer energy from one component to the next. For example, a marble rolling down a ramp will transfer kinetic energy to a lever, which then transfers that energy to a ball bearing, which transfers that energy to a spring.
The second principle involved is force. Each machine component applies force to the next component, causing it to move or change direction. For example, a ball rolling down a ramp applies force to a lever, causing it to move and trigger the next component in the chain reaction.
The third principle involved is motion. Each component of the machine is designed to move or be moved in a specific way, whether rolling, sliding, lifting, or falling. The motion of each component is carefully calculated to trigger the next component in the chain reaction.
Other scientific principles involved in this machine include friction, gravity, momentum, and potential energy. Each machine component must be carefully designed and aligned to ensure it transfers energy, applies force, and moves correctly to trigger the next component in the chain reaction.
Designing a Rube Goldberg machine involves several engineering design principles crucial to success. Here are some of the fundamental principles involved:
Creative problem-solving: The primary goal of a Rube Goldberg machine is to solve a simple problem interestingly and unexpectedly. Designers must be able to think outside the box and come up with creative solutions to achieve this goal.
Kinematics: It often relies on complex chains of cause-and-effect events. Designers must understand the principles of kinematics, which is the study of motion without considering the forces that cause that motion, to ensure that each part of the machine moves correctly and at the right speed.
Energy conversion: It often relies on the conversion of one type of energy into another. For example, potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy, or mechanical energy can be converted into electrical energy. Designers must understand the principles of energy conversion and ensure that each part of the machine can convert energy correctly.
Mechanical systems: It often relies on complex mechanical systems, such as gears, levers, pulleys, and springs. Designers must understand these mechanical systems well and how they can be used to achieve the desired result.
Materials and fabrication: They are often made from a variety of materials, including wood, metal, plastic, and paper. Designers must understand the properties of these materials and how to fabricate them in a functional and aesthetically pleasing way.
Iterative design: Designing this machine is an iterative process that involves designing, building, testing, and refining the machine until it achieves the desired result. Designers must be willing to iterate and make changes based on feedback from testing.
How to build a Rube Goldberg Machine?
How to build a Rube Goldberg Machine? Making such machine can be a fun and creative project that requires planning, experimentation, and problem-solving. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building your own machine:
Step 1: Choose a task
The first step is to choose the task that your machine will perform. It can be any simple task, such as turning on a light switch, popping a balloon, or pouring a glass of water.
Step 2: Brainstorm and sketch ideas
Next, brainstorm and sketch out ideas for each component of your machine. Think about how each component will transfer energy, apply force, and move in a specific way to trigger the next component in the chain reaction. Consider using everyday objects such as dominoes, marbles, balls, pulleys, levers, and ramps.
Step 3: Gather materials
Once you have your plan, gather the materials you will need. You can use household items such as cardboard, tape, glue, scissors, string, rubber bands, and specialized components such as motors, sensors, and microcontrollers.
Step 4: Build the machine
Begin building your machine by starting with the first component and working your way through the chain reaction. Make sure to test each component as you go to ensure that it works properly and triggers the next component in the chain reaction. You may need to adjust the components or the alignment of the machine to ensure that it works smoothly and reliably.
Step 5: Test and troubleshoot
Once the machine is complete, it’s time to test it. Trigger the first component and watch the chain reaction unfold. If the machine doesn’t work as planned, troubleshoot the problem by examining each component and making adjustments as necessary.
Step 6: Fine-tune and optimize
After you have tested the machine and made any necessary adjustments, fine-tune and optimize the machine. This involves making adjustments to the components to ensure that they work smoothly and reliably and optimizing the machine’s efficiency to make it faster and more impressive.
Step 7: Document the machine
Finally, document your machine by taking pictures or videos of it in action. You can also create a diagram or blueprint of the machine to help others understand how it works. Share your machine with others and challenge them to build their own Rube Goldberg machines.
Additional tips
Rube Goldberg machines are not just fascinating feats of engineering, but they can also be used to tell a compelling story. Here are some tips on how to use Rube Goldberg machines as a storytelling tool:
Define your message: Before you begin building your machine, define the message you want to convey. What story do you want to tell? What emotions do you want to evoke in your audience? Having a clear message in mind will help guide the design and construction of your machine.
Develop a plot: Like any good story, a machine needs a plot. This can be a simple story or a complex narrative, but it should have a clear beginning, middle, and end. Think about the characters, the setting, and the conflict that drives the story.
Incorporate themes and motifs: To make your machine more engaging and memorable, consider incorporating themes and motifs that reinforce your message. This can include visual elements, sound effects, or symbols representing your story’s fundamental ideas.
Use pacing and timing: The timing and pacing of your machine can also play an essential role in telling your story. Depending on the narrative you want to convey, you can use different speeds and tempos to create tension, suspense, or excitement.
Experiment with different components: These machines offer endless possibilities for creative expression. Don’t be afraid to experiment with other components and materials to create unique and interesting effects. This can help enhance your machine’s storytelling element and make it more memorable.
Rehearse and refine: Once you’ve built your Rube Goldberg machine, rehearse it multiple times to make sure that everything is timed correctly and that the story flows smoothly. Refine the components needed to improve the performance and ensure your message is conveyed effectively.
Examples of Rube Goldberg machines
Countless impressive Rube Goldberg machines have been created by individuals, teams, and organizations all over the world. Here are just a few examples of some Rube Goldberg machines:
- OK Go’s “This Too Shall Pass” music video – This music video features a complex machine that was created to accompany the band’s song. The machine included elements such as falling dominoes, swinging wrecking balls, and rolling billiard balls.
- The Honda “Cog” commercial – This commercial for Honda featured this machine made entirely out of car parts. It included elements such as spinning wheels, bumpers, and even an airbag.
- The “Melvin the Machine” by HEBOCON – This machine was created for the HEBOCON robot contest, which encourages participants to create low-tech, humorous robots. This machine included elements such as a seesaw, a windmill, and even a spinning chicken.
- The “The Page Turner” by Joseph Herscher – This machine was created by artist Joseph Herscher and is designed to turn a page in a book. It includes elements such as a swinging arm, a rolling marble, and a hair dryer.
- The “Rubenerd Rube Goldberg Machine” by Ruben Schade was created by blogger and programmer Ruben Schade and involved over 70 steps. It included elements such as falling marbles, swinging pendulums, and even a laser pointer.
- The “World’s Largest Rube Goldberg Machine” by Purdue University – This machine was created to celebrate the 75th anniversary of Purdue’s engineering program. It involved over 500 steps and included elements such as a giant Newton’s cradle, a rolling globe, and even a fire-breathing dragon.
- The “Red Bull Kluge” – This machine was created as a marketing campaign by Red Bull and featured a team of athletes and stunt performers. The machine included a snowboarder jumping over a giant Red Bull can, a kayaker plunging down a waterfall, and even a skydiver landing on a target.
- The “PythagoraSwitch” TV show – This Japanese television show features a the machine in each episode, with different themes and challenges. Designers and engineers create the machines, often including rolling balls, falling dominos, and moving toys.
- “The Cake Server” by Steve Price – This machine was created by artist Steve Price and is designed to cut a slice of cake. It includes elements such as a rotating platform, a sliding drawer, and a spinning balloon.
- “The Time Machine” by Joseph Herscher – This machine, also created by Joseph Herscher, is designed to pour a cup of tea. It includes elements such as a spinning bicycle wheel, a falling bowling ball, and a levitating teapot.
What skills can students learn through making a Goldberg machine?
What skills can students learn through making a Goldberg machine? Making a Rube Goldberg machine can provide an excellent opportunity for students to learn a range of skills and concepts, including:
Engineering design principles: Students can learn about engineering design principles such as problem-solving, prototyping, and testing by creating the machine.
Creative thinking and innovation: Making this machine requires students to think creatively and come up with unique and innovative solutions to each step of the machine.
Collaboration and teamwork: Building this machine is often a collaborative effort that requires students to work together and communicate effectively to achieve a common goal.
Physics concepts: Students can learn about concepts such as gravity, momentum, and energy transfer through the various elements and steps of the Rube Goldberg machine.
Persistence and perseverance: Making the machine can be a challenging and time-consuming process, but it can also teach students the value of persistence and perseverance in pursuing a goal.
Attention to detail: The creation of the machine requires careful attention to detail and precision, as each step of the machine must be precisely timed and executed for the machine to work correctly.
Presentation skills: Once the machine is completed, students can develop their presentation skills by showcasing their machine to others and explaining the various steps and elements involved.
Time management: Students must learn how to manage their time effectively when building a machine. They must set goals, prioritize tasks, and work efficiently to meet deadlines.
Critical thinking: Making the machine requires students to think critically about the various components and steps involved in the machine. They must analyze each step and identify potential problems and solutions.
Coding and programming: In some cases, these machines may involve electronic components that require coding and programming. This provides an opportunity for students to learn basic coding concepts and programming skills.
Innovation and creativity: The design and construction of such machines require a great deal of innovation and creativity. Students must develop new and inventive ways to achieve each step in the machine, which can foster creativity and innovation.
Learning from failure: Building a Rube Goldberg machine can involve many trial-and-error processes, and students must be willing to learn from their mistakes and failures. This can teach them the value of persistence, resilience, and adaptability in facing challenges.
Overall, creating this awesome machine provides an excellent opportunity for students to learn a range of valuable skills that can be applied to various areas of their academic and personal lives. It can help to promote critical thinking, creativity, innovation, teamwork, and persistence, among other valuable skills.
Having all the necessary information is essential before choosing any course of action. AdmissionSight is always here to assist you with any questions or concerns. We have more than ten years of expertise assisting students in successfully navigating the challenging admissions process.
Consult with AdmissionSight and find out what we can do to help you get into the school of your choice by ensuring that you are sufficiently aware and well-prepared for the application process.