How to Become a College Professor
Becoming a college professor is a rewarding but challenging path that requires a combination of education, experience, specialized knowledge, and dedication. This article will guide you through the steps necessary to achieve this lofty academic goal.
Understanding the Role of a College Professor
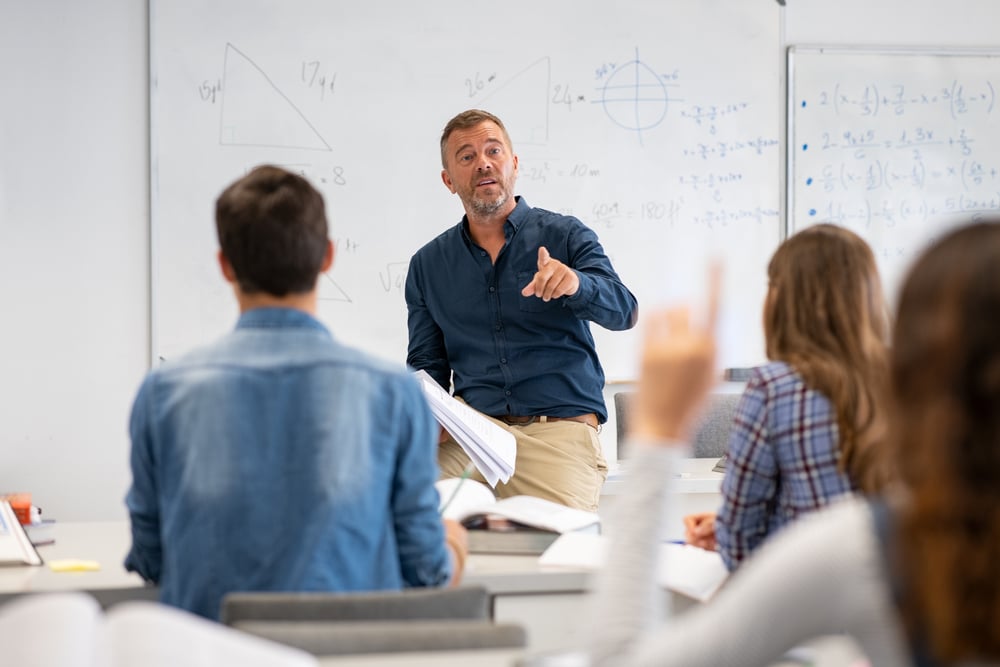
The position of a college professor is more than just instructing students. It is a combination of multiple roles that contribute towards the academic growth and development of students, the advancement of their own scholarly pursuits, as well as the betterment of their institution and the broader community.
College professors play a vital role in shaping the minds of future generations. They are not only responsible for imparting knowledge but also for fostering critical thinking, creativity, and a passion for learning. By creating a stimulating and engaging learning environment, professors inspire students to explore new ideas, challenge existing beliefs, and develop their own unique perspectives.
In addition to their teaching responsibilities, college professors are actively involved in research. They dedicate a significant amount of time to conducting studies, analyzing data, and publishing their findings in academic journals. Through their research, Professors contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields, pushing the boundaries of human understanding.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A college professor’s responsibilities vary, but most commonly include teaching undergraduate and graduate students, creating and implementing curriculum, grading assignments and exams, advising students, conducting research in their field, and publishing their findings in academic journals.
They also need to participate in department and university committees, present their research at conferences, and stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field.
Teaching is not limited to standing in front of a classroom and delivering lectures. Professors employ various teaching methods, such as group discussions, case studies, and hands-on experiments, to ensure that students actively engage with the material. They provide guidance and support, encouraging students to ask questions, seek clarification, and explore different perspectives.
In addition to these responsibilities, a professor is also expected to contribute to the institution’s reputation and success. This can often include departmental service, where Professors collaborate with colleagues to improve the curriculum, develop new programs, and enhance the overall educational experience. They also mentor junior faculty, sharing their expertise and guiding them in their career development.
Required Skills and Competencies
Becoming a successful college professor requires a unique combination of skills and competencies. Excellent written and oral communication skills are crucial, as you’ll be responsible for conveying complex theories and concepts to your students. Professors must be able to break down complex ideas into digestible pieces, ensuring that students understand and retain the information.
Research skills are equally important, as professors are expected to contribute to the growth of their field through scholarly research. They must be able to design rigorous experiments, collect and analyze data, and draw meaningful conclusions. Professors also need to stay updated with the latest advancements in their field, attend conferences, and network with other researchers.
Other important traits include critical thinking skills, problem-solving ability, passion for learning, creativity, organizational skills, and the capability to work in an interdisciplinary environment. Professors often collaborate with colleagues from different disciplines, bringing together diverse perspectives to tackle complex problems.
Furthermore, professors must be dedicated and self-motivated. They need to manage their time effectively, balancing their teaching, research, and administrative duties. The ability to prioritize tasks and meet deadlines is crucial for maintaining a successful academic career.
In conclusion, the role of a college professor extends far beyond the classroom. They are educators, researchers, mentors, and contributors to their institution and the broader academic community. Through their passion for teaching and commitment to scholarly pursuits, Professors shape the future of education and make a lasting impact on the lives of their students.
Educational Requirements for Becoming a College Professor
The journey to becoming a college professor is a rigorous and intellectually stimulating one, requiring a significant investment of time and effort.
With a commitment to lifelong learning, aspiring professors embark on a path that spans over a decade of study, research, and practical experience. This educational journey equips them with the knowledge, skills, and expertise necessary to excel in their chosen field.
Undergraduate Studies
The first step towards becoming a college professor is acquiring a bachelor’s degree. This foundational stage of education provides students with a broad understanding of their chosen field and cultivates a passion for knowledge.
During undergraduate studies, aspiring professors immerse themselves in a diverse range of subjects, from introductory courses to advanced seminars, all designed to build a solid theoretical foundation. It is during this time that students develop critical thinking skills, engage in lively debates, and begin to shape their academic interests.
Furthermore, undergraduate studies offer numerous opportunities for students to engage in extracurricular activities that enhance their academic experience. These activities may include joining research groups, participating in internships, or attending conferences and workshops. Such involvement not only expands their knowledge but also fosters valuable connections with professors and professionals in their field.
Graduate Studies
Following the successful completion of an undergraduate degree, prospective professors embark on the next phase of their educational journey: graduate studies. Pursuing a Master’s degree in their chosen field allows students to delve deeper into their specialty, exploring advanced concepts and methodologies. This stage of education encourages independent thinking, original research, and critical analysis.
Graduate students often have the opportunity to collaborate with renowned professors and researchers, contributing to ongoing projects and gaining valuable insights into the academic world. Additionally, they may have the chance to present their research findings at conferences or publish them in reputable academic journals. These experiences not only bolster their academic credentials but also establish their presence within the scholarly community.
Postdoctoral Experience
After obtaining a doctoral degree, most aspiring professors engage in postdoctoral experience. This phase of their journey involves conducting research under the guidance of established academics and may also include teaching responsibilities. Postdoctoral experience provides a unique opportunity for individuals to further refine their research skills, expand their academic network, and gain exposure to different teaching methodologies.
During this period, postdoctoral fellows often collaborate with experts in their field, contributing to groundbreaking research projects and making significant contributions to their respective disciplines. They may also have the chance to mentor undergraduate and graduate students, sharing their knowledge and expertise while honing their teaching abilities.
This multifaceted experience not only strengthens their research portfolio but also prepares them for the challenges and responsibilities of a future academic career.
In conclusion, the educational requirements for becoming a college professor are demanding but rewarding. The combination of undergraduate studies, graduate studies, and postdoctoral experience provides aspiring professors with a comprehensive education that prepares them for a successful and fulfilling career in academia.
Through their unwavering dedication to learning, research, and teaching, these individuals contribute to the advancement of knowledge and inspire future generations of scholars.
The Importance of Specialization
Having a specialization in your chosen field is pivotal to becoming a professor. Universities look for individuals who can bring a depth of knowledge and research in a specific area, and it also allows individuals to distinguish themselves in today’s competitive academic job market.
Specializing in a particular field not only enhances your expertise but also opens up numerous opportunities for growth and advancement in your academic career. By focusing your studies and research on a specific area, you can delve deeper into the subject matter, uncovering new insights and contributing to the existing body of knowledge.
Choosing a Field of Study
Choosing a field of study is a critically important step in your journey to become a college professor. Ideally, this should be a field you’re passionate about, as you’ll be dedicating a significant portion of your life to studying and teaching this subject matter.
When selecting a field of study, it’s essential to consider your interests, strengths, and long-term goals. Reflect on what fascinates you the most and what you can envision yourself dedicating countless hours to researching and teaching. Additionally, it’s beneficial to explore the current trends and demands in academia to ensure that your chosen field aligns with the needs of the academic community.
Moreover, it’s worth noting that choosing a field of study is not a one-time decision. As you progress in your academic career, you may find yourself drawn to different subfields or areas of specialization within your chosen discipline. Embrace these opportunities for growth and adaptability, as they can lead to a more well-rounded and versatile academic profile.
Staying Current in Your Field
As a college professor, it’s crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in your field. This ongoing learning involves regularly reading scholarly journals, attending conferences and symposiums, engaging with your academic community, and continually pursuing your own research endeavors.
By staying current in your field, you not only expand your knowledge but also foster connections with other experts in your discipline. Attending conferences and symposiums allows you to exchange ideas, collaborate on research projects, and gain valuable insights from colleagues who share your passion for the subject matter.
Furthermore, engaging with your academic community through discussions, seminars, and workshops can provide a platform for intellectual growth and stimulate new research directions. It also allows you to contribute to the academic community by sharing your own expertise and insights.
Additionally, pursuing your own research endeavors is vital for personal and professional development. Conducting research not only adds to the existing body of knowledge but also hones your critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It allows you to contribute to the advancement of your field and establish yourself as an authority in your area of specialization.
In conclusion, specialization plays a crucial role in the journey of becoming a college professor. It provides depth of knowledge, distinguishes individuals in the competitive academic job market, and opens up opportunities for growth and advancement. Choosing a field of study should be driven by passion and long-term goals while staying current in your field involves continuous learning, engagement with the academic community, and pursuing your own research endeavors.
The Path to Tenure
Achieving tenure is often considered the crowning achievement in an academic career. It provides job security and the freedom to pursue research interests without the worry of contract renewal or termination.
But what exactly does the path to tenure entail? Let’s delve deeper into the tenure track process and the expectations that come with it.
The Tenure Track Process
The tenure track is a defined pathway that leads to tenure status at a university. It usually begins with a position as an assistant professor, progresses to an associate professor, and finally, to a full professor. Each step along this journey comes with its own set of responsibilities and expectations.
As an assistant professor, individuals are expected to demonstrate their potential for excellence in teaching, research, and service to the university community. This is a crucial period where they have the opportunity to establish their reputation and make significant contributions to their field.
Advancing to the rank of associate professor requires a continued commitment to excellence in teaching and research. At this stage, individuals are expected to have a solid publication record and a growing reputation in their area of expertise.
Finally, reaching the rank of full professor is the pinnacle of the tenure track process. By this point, individuals are recognized as leaders in their field, with a substantial body of high-quality research, a proven track record of effective teaching, and a significant contribution to the university community.
Research and Publication Expectations
A significant portion of attaining tenure involves the publication of original research findings in reputable scholarly journals. It is important to understand that the quality of research output often carries more weight than the quantity.
Faculty members seeking tenure are expected to engage in rigorous and impactful research that advances knowledge in their field. This research should demonstrate originality and significance and contribute to the broader academic community.
Furthermore, the publication process itself can be a challenging and time-consuming endeavor. It involves conducting experiments, analyzing data, writing manuscripts, and navigating the peer-review process. Successful tenure candidates are those who can effectively manage their time and resources to produce high-quality publications.
In addition to research, teaching is another critical aspect of the tenure track process. Faculty members are expected to excel in the classroom, engaging students and fostering a positive learning environment. Effective teaching evaluations and innovative pedagogical approaches can greatly enhance a candidate’s chances of obtaining tenure.
Lastly, service to the university community is an essential component of the tenure track process. This can include serving on committees, participating in departmental activities, mentoring students, and engaging in outreach efforts. Active involvement in the university community demonstrates a commitment to the institution’s mission and values.
In conclusion, the path to tenure is a multifaceted journey that requires dedication, hard work, and a commitment to excellence in teaching, research, and service. It is a process that spans several years, with each step building upon the accomplishments of the previous one. Attaining tenure is not only a professional milestone but also a testament to an academic’s contributions and impact in their field.
The Job Market for College Professors
The job market for Professors is, generally speaking, quite competitive. The number of people obtaining PhDs continues to grow, while tenure-track positions are not expanding at the same rate.
Job Prospects and Competition
While competition for tenure-track positions is high, there are numerous job opportunities in academia. This includes adjunct or visiting professorships, teaching at community colleges, administrative roles within universities, research positions, or roles in related industries.
Geographic Considerations
It’s also important to consider geographic flexibility. Being open to relocation can greatly increase the number of job opportunities available. That said, job availability will always depend on the field of study and the current market demand for those specialties.
Through education, experience, skill development, careful planning, and a true passion for their chosen field, anyone interested in academia can aspire and work to become a college professor. It’s a fulfilling role that leaves a significant impact on the lives of students and the growth of knowledge in society.
Having all the necessary information is important before choosing any course of action. AdmissionSight is always here to assist you with any questions or concerns. We have more than ten years of expertise assisting students in successfully navigating the challenging admissions process.
Consult with AdmissionSight and find out what we can do to help you get into the school of your choice by ensuring that you are sufficiently aware and well-prepared for the application process.